Unlocking the power of survey logic: A guide to effective surveys
Are you struggling with low survey completion rates and inaccurate data? It might be time to unlock the power of survey logic. This powerful feature increases survey efficiency, improves respondent experience, and leads to more reliable results. In this article, we take a deep dive into the world of survey logic, covering the essentials, implementation, customization, benefits, best practices, and common mistakes to avoid. By the end of this post, you will have the knowledge you need to create more effective surveys and get the most out of your survey data.
Key takeaways
- Survey logic is an essential tool for creating effective research.
- Skip, branching and piping logic can create a personalized survey experience that balances personalization and simplicity.
- Careful planning of survey flow is key to avoiding common mistakes such as too many rules, creating circular loops or mixing hide/skip logic.
- Our experience proves that skip logic plays an important role when conducting NPS surveys. Each feedback with average or poor score triggers an automated e-mail notification to our customer care. This not only helps us respond to any issue in time but also provides valuable insights to increase customer retention and improve user engagement.
The Essentials of survey logic
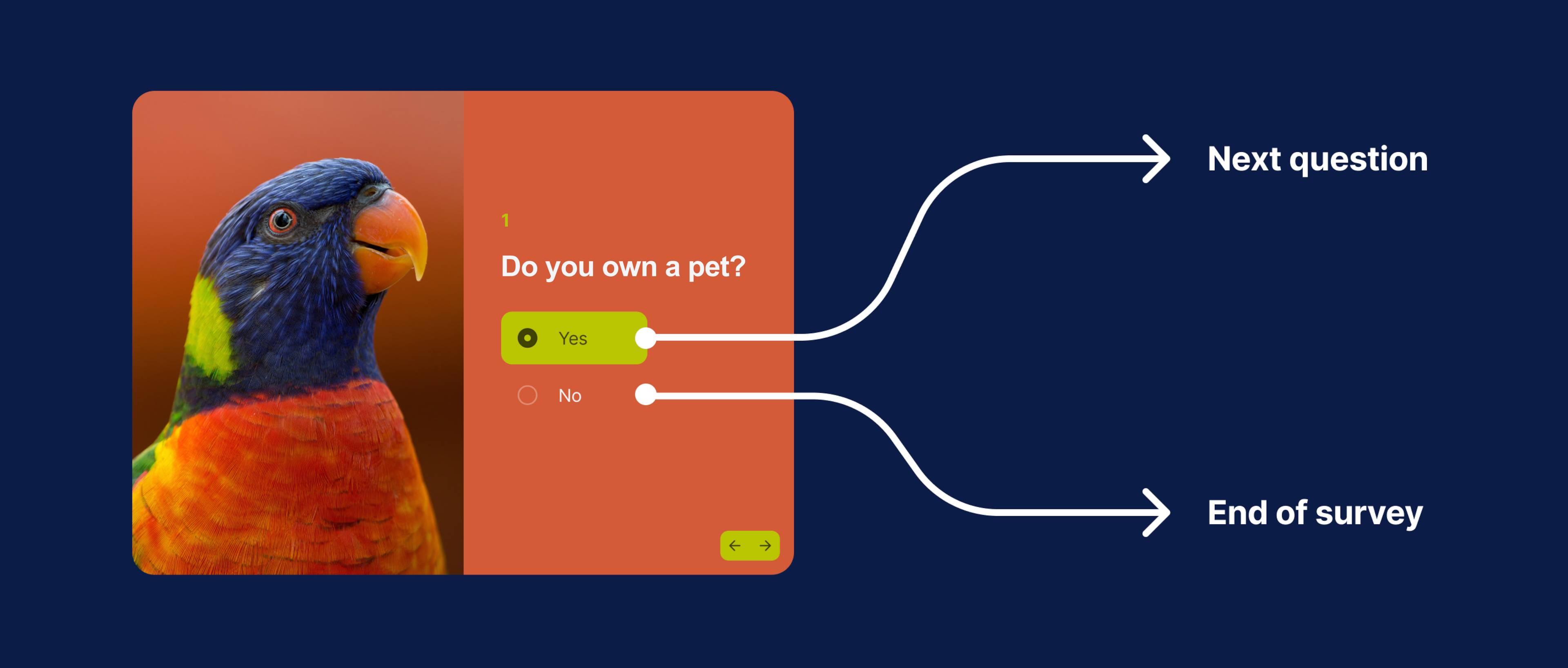
Survey logics is an effective tool that can shape your survey based on respondents’ answers, ensuring they only encounter questions relevant to their experiences. By incorporating various logic rules, you can provide a seamless and engaging survey experience for your respondents, ultimately leading to higher completion rates and more accurate data. Using the right survey language, it is possible to further enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your surveys.
The main types of survey logic are:
- skip logic,
- branching logic, and
- piping logic.
Let’s explore each of these techniques to grasp the fundamentals of survey logic in general.
Skip logic

Skip logic, also known as conditional branching, allows you to design surveys in a way that enables respondents to skip over irrelevant questions and proceed to the next relevant section of the survey. This technique helps improve survey efficiency by ensuring that respondents only answer questions applicable to their situation.
Example:
If you ask respondents whether or not they have ever traveled to Europe and they answer “No,” with skip logic in place, the subsequent questions about details regarding European traveling experience can be skipped.
Branching logic

Branching logic is another powerful technique that directs respondents to relevant follow-up questions based on their answers to a multiple-choice question or other types of questions. This personalization ensures that respondents only view questions pertinent to their prior responses, which can serve as a motivator to answer your survey. As a result, you will receive reliable feedback and accurate data for subsequent analysis. Implementing branching logic also creates a more engaging survey experience and increases the likelihood of survey completion.
Example:
You have been assigned to conduct a survey for an HR agency. The opening question might start “Are you an employer or an employee?”. Depending on the answer, branching logic could direct respondents to an entirely different set of questions tailored either to employers or employees.
Piping logic

Piping logic is a technique that incorporates one answer from a previous question into subsequent questions, providing a more personalized interaction for respondents. This technique can be particularly useful when asking follow-up questions based on previous answers, creating a sense of continuity and relevance throughout the survey.
The use of piping logic helps you create a dynamic set of questions that adapt on the fly, resulting in richer data collection and deeper insights without extending the overall length of your survey.
Example:
When a respondent indicates in a question regarding color preference that their favorite color is blue, a later question will use this information to ask this way: “Why do you prefer blue over other colors?”
Once you decide to add survey logic in your surveys, you will see that it is not difficult at all. Let’s take Survio as a well-known survey software to set an example. All you need to do is click on the question to which the rule is to be applied, select “Logic” and choose the appropriate action. Feel free to broaden your horizons by other practical examples on survey logic.
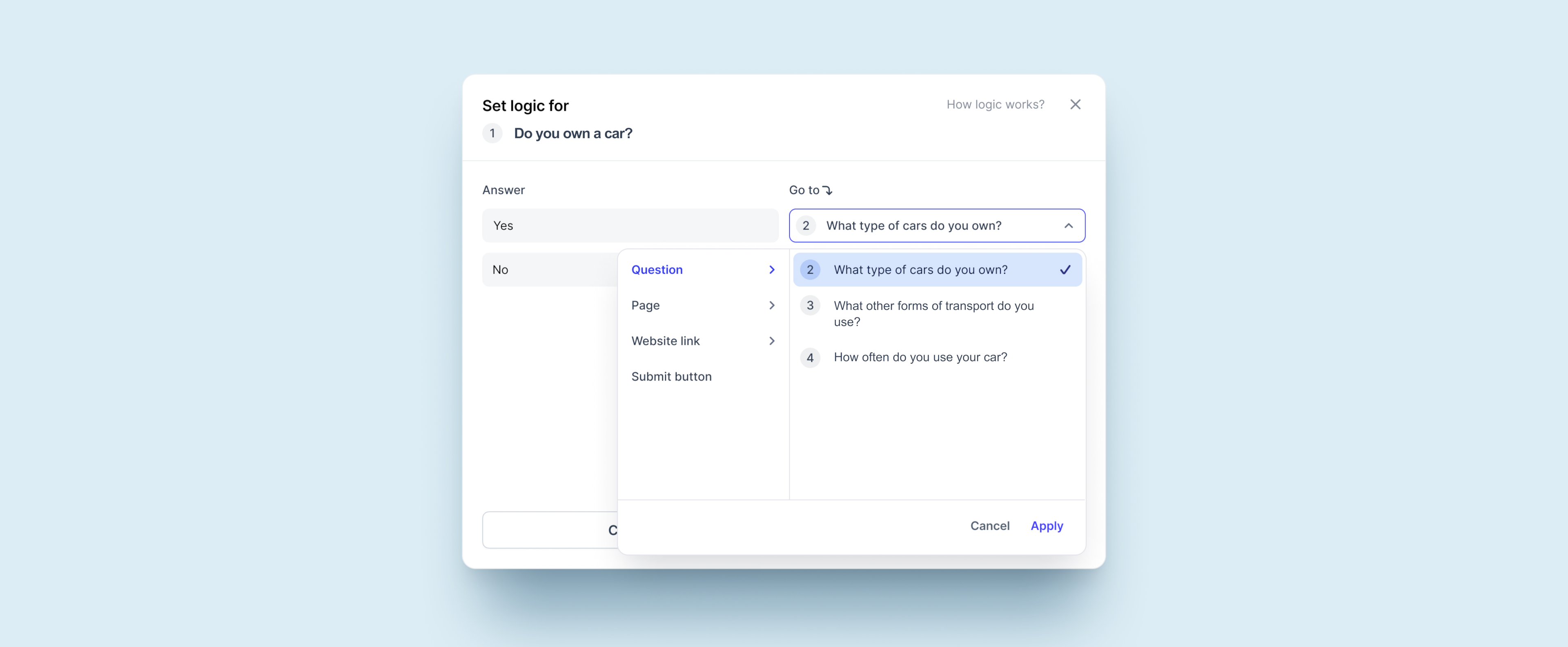
Implementing survey logic rules
Now that you are familiar with the basics of survey logic, it is time to learn how to implement these rules in your survey. Implementing survey logic rules involves setting up actions and criteria for multi-question and single-question branching, which can be combined using AND/OR logic. Let’s take a closer look at the different ways to implement survey logic rules.
Multi-question branching
Multi-question branching is a type of branching logic that directs respondents to different sets of questions based on their answers to prior questions. This technique is particularly useful in the following cases, when you want to:
- create a highly tailored survey experience for respondents with different backgrounds or interests,
- gather specific information from different groups of respondents,
- save time by skipping irrelevant questions for certain respondents.
By using multi-question branching, you can ensure that each respondent receives a survey that is relevant to their needs and interests.
Single-question branching
Single-question branching is another type of branching logic that determines the next question shown based on a respondent’s answer. This technique simplifies the feedback process for respondents by allowing them to seamlessly move on to the next relevant question.
When implementing multi-question or single-question branching, it is important to create relevant and necessary logic rules to avoid overcomplicating your survey. Effective use of multi-question branching increases survey relevance, reduces survey fatigue, and improves data accuracy.
Combining AND/OR logic
Combining AND/OR logic allows for more complex survey logic rules and conditions, enabling you to create highly customized survey journey for a wide range of respondents.
- The AND operator is used to combine multiple conditions, i.e. all conditions must be true for the overall condition to be true.
- The OR operator, on the other hand, requires only one condition to be true for the overall condition to be true.
Customizing your survey with logic
Customizing your surveys by adding logic to questions, managing multiple rules, and testing and refining the rules’ framework is essential for creating a smooth, highly engaging, and relevant interaction for your respondents.
Let’s delve deeper into the process of tailoring your survey with logic and custom data, and explore some best practices for each step.
Adding logic to questions
Adding logic to questions is the next step in customizing your survey. While various online survey platforms have differenct user interfaces for creating specific conditions within the survey flow, the overall process is generally the same.
- Select the desired question and look for the “Logic” icon in its settings.
- Click this icon to add logic to the question.
- Configure the necessary actions for each question and ensure that they remain relevant to each respondent’s answer.
When adding logic to questions, it is advisable to strike a balance between creating a personalized survey experience and avoiding unnecessary complexity.
Managing multiple rules
Managing multiple rules is an essential skill when applying logic to your surveys. To create and organize multiple rules, you will need to consider their order, making sure that the survey unfolds logically and smoothly.
Testing and refining logic
Testing and refining logic is inevitable, as it ensures that your survey logic works correctly and provides a seamless interaction for your respondents. To test and refine your logic, consider checking your survey in a preview mode or running it with test respondents, making any necessary adjustments based on their feedback.
Additionally, it is recommended that youproperly document your logic for the purpose of tracking changes. This will make the entire survey logic frame accurate, efficient, and effective.

Survey logic benefits and best practices
Survey logic has many benefits, such as enhancing survey relevance, reducing survey fatigue, and increasing data accuracy. Its use creates a more engaging and efficient survey experience for respondents, which ultimately leads to more reliable results.
To make the most of these benefits, it is worthwhile to follow some of the best practices.
Enhancing survey relevance
Enhancing survey relevance results in enabling your respondents to only answer questions that are applicable to them, which can greatly improve survey engagement and response rates. By implementing skip logic, branching logic, and piping logic, you can create a highly personalized survey journey that caters to each respondent’s unique needs and preferences.
Reducing survey fatigue
Reducing survey fatigue is paramount to preventing survey dropouts and improving response rates. By eliminating irrelevant survey questions and streamlining the question flow, you will keep your respondents engaged and motivated to complete your survey.
Additionally, it is essential to keep your survey concise and straightforward, avoiding unnecessary complexity and repetitiveness. Focusing on reducing survey fatigue increases the likelihood of survey completion and improves the overall data quality.
Increasing data accuracy
Increasing data accuracy is crucial for obtaining reliable and actionable insights from your survey data. By asking relevant questions and tailoring your survey to each respondent’s unique situation, you will collect more accurate and reliable data.
Adding logic can help you achieve this goal by ensuring that respondents only encounter questions applicable to their experiences. Additionally, it is essential to test and refine your survey logic to keep it accurate and effective.
Focusing on increasing data accuracy yields more reliable and valuable insights from your survey data.
Common survey logic mistakes to avoid
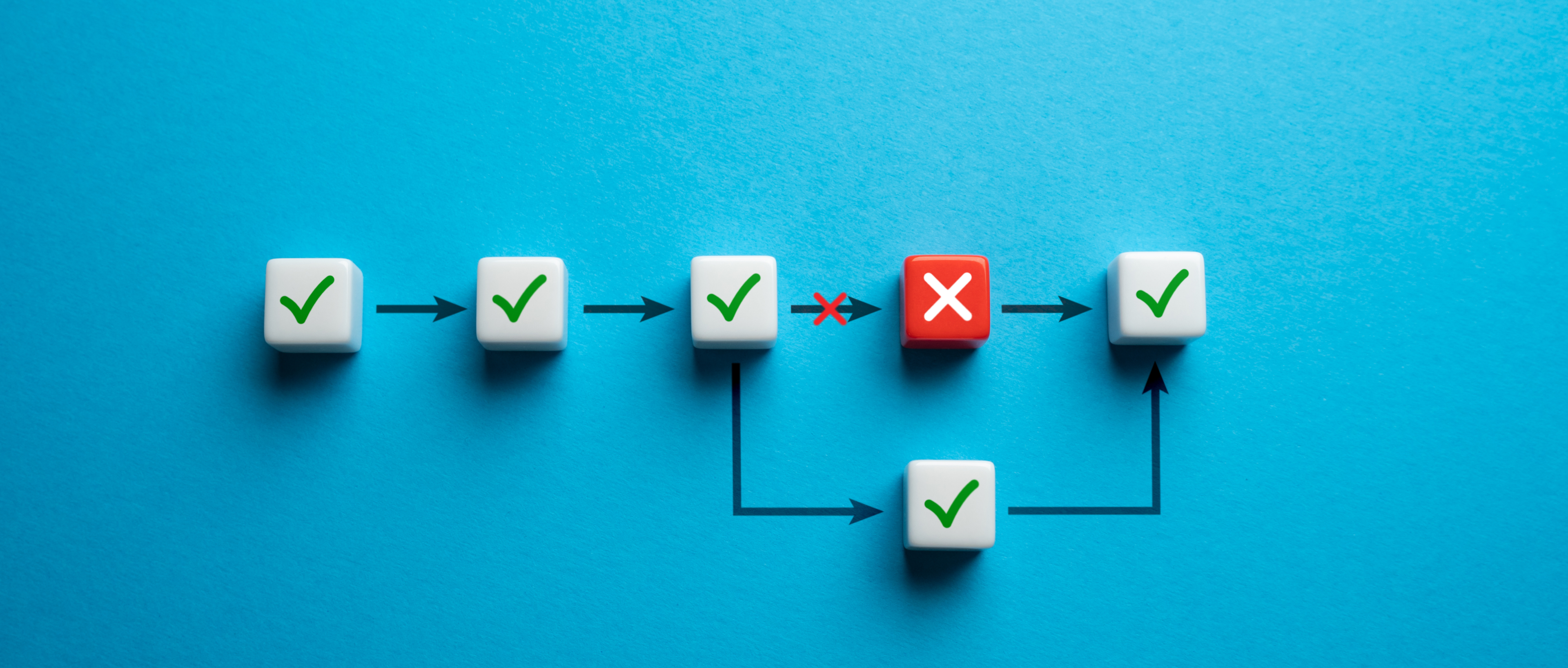
While survey logic offers many benefits, it is essential to be aware of common mistakes to avoid when using this feature. Some common survey logic mistakes include overusing logic rules, creating loops, and mixing hide logic with skip logic.
Being aware of these pitfalls and following best practices ensures a smooth and efficient survey flow for your respondents. To avoid common mistakes, it is crucial to test your survey early and explore the potential issues that may arise.
Overusing logic rules
Overusing logic rules can make your survey overly complex and difficult to manage, leading to a confusing and frustrating experience for your respondents. To avoid this pitfall, only use necessary logic and strike a balance between personalization and simplicity.
Careful selection and implementation of logic rules will create a more engaging survey journey for your respondents, which can positively impact your Net Promoter Score. Read more about the Net Promoter Score as a standardized loyalty metric.
Creating loops
Creating loops can prevent surveys from being completed, as respondents can get stuck in a loop and be unable to continue answering. To avoid this issue, make sure that your survey logic moves respondents forward in the survey instead of looping back to previous questions.
Mixing hide and skip logic
Mixing hide and skip logic can cause confusion and disrupt the flow of your survey, leading to a less engaging experience for your respondents. To avoid this issue, use hide and skip logic separately so that each serves a distinct purpose in your survey design.
Proper use of logic rules, avoiding loops, and careful selection and implementation of hide and skip logic enhance the respondent experience while taking surveys. This provides more feedback, delivering richer insights into surveyed areas.
Summary
In conclusion, survey logic is a powerful tool that can greatly improve the effectiveness, relevance, and accuracy of your surveys. By understanding the basics of survey logic, implementing and customizing your surveys with logic, and avoiding common mistakes, you will create a more engaging and efficient survey experience for your respondents. As a result, you will collect more reliable and actionable data that will drive your decision-making and bring positive results for your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a survey logic?
Survey logic is a way to modify survey behavior or content based on respondent answers. It allows for pages to be skipped, questions to be displayed, quotas to be set and notifications to be sent.
What is an example of survey logic?
An example of survey logic is creating a logic flow to hide gender-specific questions from respondents based on their gender, so that female respondents only see relevant questions for them, and male respondents see relevant questions for them.
Can I apply multiple logic rules to a single question?
Yes, many survey platforms allow for the application of multiple logic rules to a single question. However, it is crucial to pay attention that these rules do not conflict with each other, leading to a confusing respondent experience.
How do I know if my survey logic is working correctly?
It is recommended to thoroughly test your survey before distributing it. This involves checking it in a preview mode, taking it multiple times, simulating different respondent paths to make sure that all logic rules work as intended.
Can I change survey logic after I have started collecting responses?
Modifying logic after starting data collection can lead to inconsistencies in your data. If changes are necessary, it is best to clearly note when they were made and consider starting a new data collection phase.
Create your own questionnaire or survey for free
Setting up your first survey is quick and straight forward. Choose from one of 100 predefined templates or create your own from the scratch. Start getting your first responses in 5 minutes.
Create your own survey




